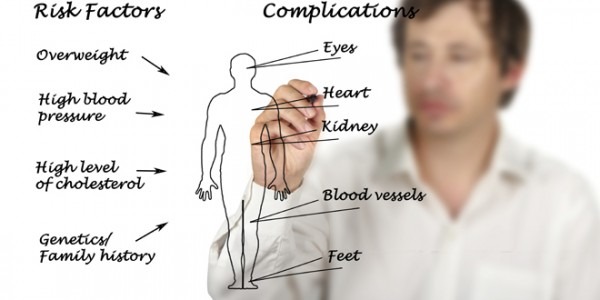
Complications of diabetes often develop gradually, and happen when blood glucose levels are consistently too high (this is called hyperglycemia). The longer you have diabetes – and the less controlled your blood glucose levels – the higher the risk of complications.
Possible complications due to continuously high blood glucose levels can include:
- Cardiovascular disease, including angina, heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis)
- Eye damage (retinopathy)
- Kidney disease (nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
For people with diabetes who take insulin, hyperglycemia can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Not taking enough insulin to match food intake
- Inaccurate insulin dosage calculations
- Forgetting to take injections or boluses
- Not performing enough self-monitoring blood glucose tests
To minimize the risk of complications caused by hyperglycemia, the most important thing that people with diabetes can do is ensure that their A1C and blood glucose levels are in their target range. In fact, numerous studies have shown that lower A1C is associated with a lower risk of developing long-term diabetes complications. (For more information about A1C, click here.)
The three main ways you can help maintain target blood glucose levels and prevent complications are to:
- Eat healthy meals
- Exercise regularly
- Take your diabetes medications or insulin as recommended by your healthcare team
For people who take insulin to manage their diabetes, an insulin pump can help you control your blood glucose levels, and avoid or delay the complications of diabetes. Most experts agree that a pump is one of the best ways to take insulin, as it can deliver insulin in a continuous manner. That’s why an insulin pump is recommended for people who have problems with blood sugar highs or lows, or those who can’t get good control with insulin injections despite their best efforts.
A number of studies have shown that continuous insulin delivery – such as that delivered by an insulin pump – can regulate blood glucose levels and prevent or delay the complications of diabetes. In fact, one of the most important, long-term diabetes studies conducted – the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial – showed overwhelmingly that intensive insulin therapy reduced the risk of complications in people with diabetes, including cardiovascular disease, retinopathy and neuropathy.
In general, you may be able to achieve better control with an insulin pump if you experience any of the following:
Concerns about, or symptoms of, long-term complications
- Fear of needles
- Difficulty managing highs and lows
- Fear of hypoglycemia, especially at night
- A1C and blood glucose levels above target
If you think that an insulin pump might help you keep your A1C and blood glucose levels in their target ranges, talk to your healthcare team.
This article was sponsored by an unrestricted educational grant from Animas Canada.
 Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care
Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care