
Did you know?
All people living with diabetes should have targets set for their diabetes, this is especially true as people get older.
- Ask your diabetes team what blood sugar level is best for your family member.
- The older people get, the less they are alike: you may know other people who have diabetes who will have different blood sugar targets.
- insulin, in the prescribed dose, does not circulate in the baby’s blood1, 2
- Tell the health care team if your family member is having any blood sugar levels below their target.
Did you know?
As people get older they sometimes worry about their memory.
- When insulin is added as treatment, it is a change in routine. Some older adults may have trouble remembering whether they took their insulin. One memory aid for remembering insulin injections is a dosette – place an insulin pen needle tip into each compartment for the week. Both you and your loved one can check to ensure the needle has been used.
- Another option is to use an insulin pen that has a memory feature.

Did you know?

Depression is common in older adults
- Depression can interfere with older adults ability for self-care.
- Untreated depression can make it difficult for older adults to go to the grocery store to buy food, for example, or can interfere with their motivation to take insulin injections.
Signs of depression in older adults can be different than in younger adults and can include:
- early morning awakening
- Tphysical complaints
- lack of appetite
- weight loss
- substance abuse
Other considerations
If injecting themselves:
- Encourage them to attend their clinic appointments with their insulin and supplies.
- Ask them to show you how they inject every 3-6 months to ensure that they are not missing any important steps (i.e. priming, mixing cloudy insulin, rotating injection sites or using a new needle every time).
- Use of a short needle is recommended. In lean older adults a skin lift may be necessary to reduce the risk of injecting into a muscle.
If you, or a family member is performing the injection:
- Consider the use of a safety engineered device to prevent needlestick injuries.
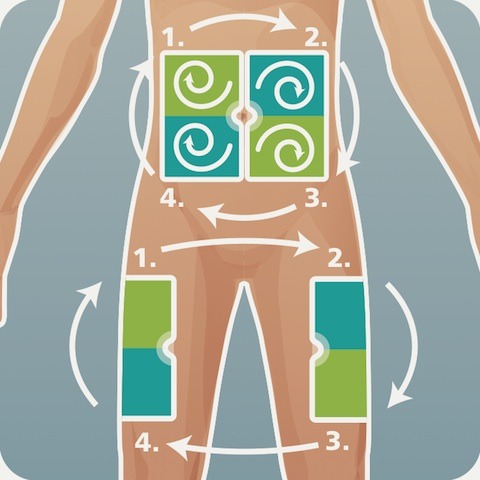
- Ensure that a site rotation routine is set. This will ensure proper absorption of insulin and prevent unnecessary problems at the injection site.
Did you know?
Technology is improving for older adults living with diabetes.
- The diabetes health care team can help find the best delivery device for your family member.
- There is a lot to learn about using insulin and devices. Give your family member lots of time and practice to learn these skills. Encourage them to ask questions if they are not sure about something.
Supported by BD Medical – Diabetes Care
02-2014
 Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care
Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care



