How well do you hear?
Have you started to notice that your hearing is not as good as it used to be? To help gauge your hearing health, consider the following questions:
- Do you have difficulty following conversations in a restaurant, a large group situation, or when there is background noise?
- Do you often ask others to repeat themselves?
- Have people ever told you that you listen to the television or radio too loud?
- Have you been told that you speak too loudly?
- Do you find it difficult communicating using a telephone?
If you answer ‘yes’ to any of these questions, you may benefit from a hearing evaluation from a hearing care professional.
Hearing loss statistics
Approximately 54% of Canadians between the ages of 40 and 79 have at least mild hearing loss, while 93% of Canadians between 70 and 79 years of age have hearing loss. Treating your hearing loss is absolutely vital. According to a recent study conducted by the National Council on Aging, people who do not treat their hearing loss are more likely to experience higher rates of depression, anger, paranoia and other psychological and emotional distresses, versus those who do. Surprisingly, only 20% of people with hearing difficulties seek help and take advantage of today’s modern hearing health technology.
Hearing aids
Hearing aids are the most common treatment for hearing loss. They are helpful for people who live with sensorineural hearing loss, which is caused by exposure to loud noises, a family history of hearing loss, the natural aging process, or a disease that can cause nerve damage, such as diabetes. Imagine enjoying sounds you have not heard in ages – such as birds chirping, friends talking, and grandchildren laughing.
Hearing aids work by amplifying sound through a three-part system:
- A microphone picks up sounds in the environment
- An amplifier makes the sounds louder
- A receiver sends these amplified sounds into the ear
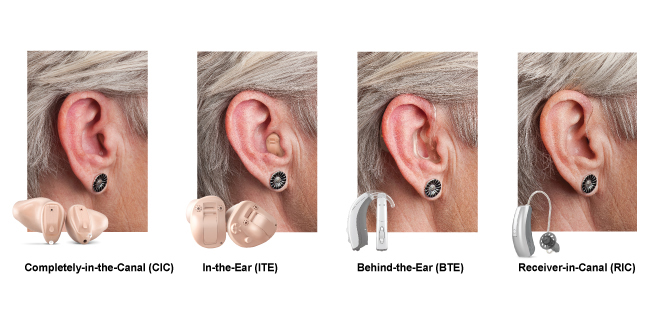
Types of hearing aids
Hearing aids are available in a range of sizes and power levels. These days, they are generally very small and discreet, and some can fit inside the ear. Hearing aids use either replaceable batteries or rechargeable batteries; with rechargeable batteries, the hearing aids are placed in a charging unit overnight, so they are ready to be used in the morning. Many modern versions of hearing aids can also distinguish background sounds (such as music or traffic) from foreground sounds (such as speech).
There are different styles of hearing aids. A hearing care professional can recommend the best type of hearing aid based upon lifestyle, hearing needs and personal preference. These include:
- Completely-in-the-canal hearing aids are a more discreet option; they are essentially smaller versions of in-the-ear hearing aids: they fit deeper into the ear, making them less visible.
- In-the-ear hearing aids are small hearing aids that are custom fitted to fully fit inside your ear. They can be worn for most types of hearing losses.
- Behind-the-ear hearing aids hook over the top of the ear and rest behind the ear. A small tube connects the hearing aid to a custom earpiece, called an ear mold, which fits into the ear canal. The sound from the device is either electrically or acoustically routed to the ear.
- Receiver-in-canal hearing aids are by far the most popular type of hearing aids available today. The electronics sit in a small case behind the ear and come in a variety of colours. You can match the case to your hair colour to blend in or go for a bold colour choice. A discreet wire goes over the ear and is held in place by either a rubber dome or custom tip inside the ear. These hearing aids can be almost invisible and are suitable for most types of hearing loss.
Advances in hearing aid technologies
Thanks to advances in hearing aid technologies, there are a number of possibilities to consider when selecting hearing aids.
Design and portability: Modern hearing aids are sleek and discreet. Many have a rechargeable option; some chargers are wireless and portable. In some models, a four-hour charge can provide between 16 and 20 hours of use depending on streaming time.
Bluetooth connectivity: Many hearing aids can connect to audio equipment, remote controls, televisions, and mobile or landline phones.
Durability: Some hearing aids have an advanced water-resistant coating with stainless-steel receivers that resist moisture; this reduces corrosion and enhances durability.
True artificial intelligence: Hearing aids can now automatically adapt to specific listening requirements without pushing any buttons.
Fingertip control using an app: Some new models of hearing aids can be fully controlled or fine-tuned using an app that is easily installed on a smart phone.
Medical treatment of hearing loss
It is important to have a hearing assessment and consultation with a hearing care professional, as they will perform a comprehensive hearing evaluation, help you understand the full nature of your current hearing health and recommend the best solutions to help your unique needs, depending on the nature and severity of your hearing loss.
If you suspect that you have hearing loss, contact a hearing care professional at Lifestyle Hearing for a screening test.
 Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care
Diabetes Care Community Learn, connect and care